4. Prototype
- Intent:
- Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new objects by copying this prototype.
- Applicability:
- when the classes to instantiate are specified at run-time, for example, by dynamic loading
- to avoid building a class hierarchy of factories that parallels the class hierarchy of products
- when instances of a class can have one of only a few different combinations of state. It may be more convenient to install a corresponding number of prototypes and clone them rather than instantiating the class manually, each time with the appropriate state.
- Structure:
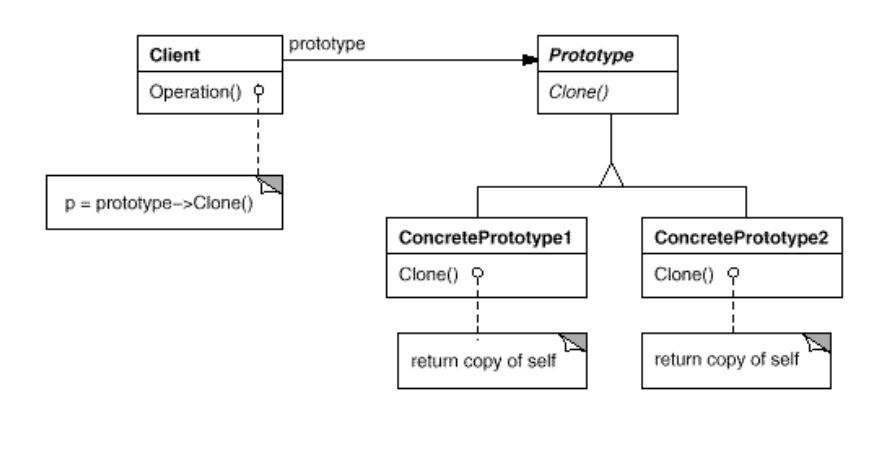
- Participants:
- Prototype (Graphic)
- declares an interface for cloning itself.
- ConcretePrototype (Staff, WholeNote, HalfNote)
- implements an operation for cloning itself.
- Client (GraphicTool)
- creates a new object by asking a prototype to clone itself.
- Prototype (Graphic)
- Collaborations
- A client asks a prototype to clone itself.
- Consequences:
-
- Adding and removing products at run-time.
-
- Specifying new objects by varying values.
-
- Specifying new objects by varying structure.
-
- Reduced subclassing.
-
- Configuring an application with classes dynamically.
-
- Related Patterns:
- Prototype and Abstract Factory are competing patterns in some way, however, they can also be used together
- Designs that make heavy use of the Composite and Decorator patterns often can benefit from Prototype as well.
Interaction diagram
-
Code Sample
public class Prototype implements Cloneable {
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Prototype proto = (Prototype) super.clone();
return proto;
}
}public class Prototype implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String string; private SerializableObject obj; /* Shallow Copy*/ public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Prototype proto = (Prototype) super.clone(); return proto; } /* Deep Shallow Copy */ public Object deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { /* output stream */ ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); oos.writeObject(this); /* input stream */ ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); return ois.readObject(); } public String getString() { return string; } public void setString(String string) { this.string = string; } public SerializableObject getObj() { return obj; } public void setObj(SerializableObject obj) { this.obj = obj; }}
class SerializableObject implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
