7. Bridge
- Intent:
- Decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently.
- Also Known As
- Handle/Body
- Applicability:
- you want to avoid a permanent binding between an abstraction and its implementation.
- both the abstractions and their implementations should be extensible by subclassing.
- changes in the implementation of an abstraction(interface) should have no impact on clients
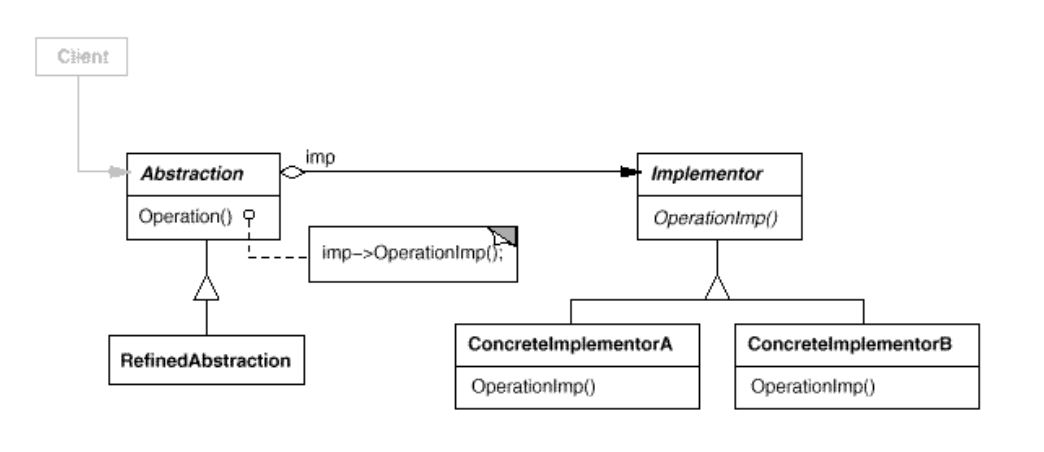
- Structure:
- Participants:
- Abstraction
- defines the abstraction’s interface(abstract class in JAVA).
- maintains a reference to an object of type Implementor.
- RefinedAbstraction
- Extends the interface defined by Abstraction.
- Implementor
- defines the interface for implementation classes.Typically the Implementor interface provides only primitive operations, and Abstraction(abstract Class in Java) defines higher-level operations based on these primitives.
- ConcreteImplementor
- implements the Implementor interface and defines its concrete implementation.
- Abstraction
- Collaborations
- Abstraction forwards client requests to its Implementor object.
- Consequences:
- 1.Decoupling interface(Abstract Class in Java) and implementation.
-
- Improved extensibility.
-
- Hiding implementation details from clients.
- Related Patterns:
- An Abstract Factory can create and configure a particular Bridge.
- The Adapter pattern is geared toward making unrelated classes work together. It is usually applied to systems after they’re designed. Bridge, on the other hand, is used up-front in a design to let abstractions and implementations vary independently.
- Code Sample: Bridge
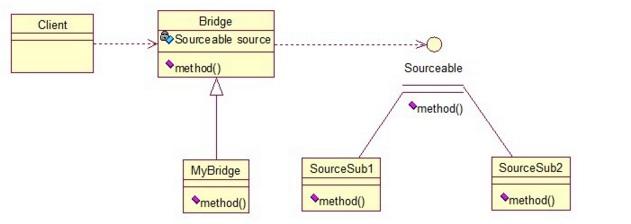
// Sourceable Interface
public interface Sourceable {
public void method();
}
// Implementors
public class SourceSub1 implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("this is the first sub!");
}
}
public class SourceSub2 implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("this is the second sub!");
}
}
//Abstract Class
public abstract class Bridge {
private Sourceable source;
public void method(){
source.method();
}
public Sourceable getSource() {
return source;
}
public void setSource(Sourceable source) {
this.source = source;
}
}
//Extention
public class MyBridge extends Bridge {
public void method(){
getSource().method();
}
}
//Test
public class BridgeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bridge bridge = new MyBridge();
Sourceable source1 = new SourceSub1();
bridge.setSource(source1);
bridge.method();
Sourceable source2 = new SourceSub2();
bridge.setSource(source2);
bridge.method();
}
}
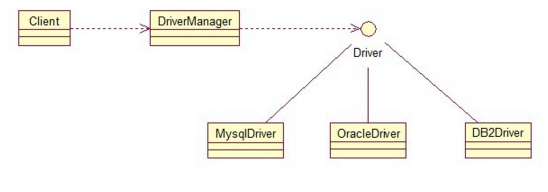
JDBC uses the bridge pattern: