12. Proxy
- Intent:
- Provide a surrogate[ˈsʌrəgət] or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
-Also Known As: - Surrogate
- Applicability:
- A remote proxy provides a local representative for an object in a different address space.
- A virtual proxy creates expensive objects on demand.
- A protection proxy controls access to the original object.
- A smart reference is a replacement for a bare pointer that performs additional actions when an object is accessed.
- counting the number of references to the real object so that it can be freed automatically when there are no more references
- loading a persistent object into memory when it’s first referenced.
- checking that the real object is locked before it’s accessed to ensure that no other object can change it.
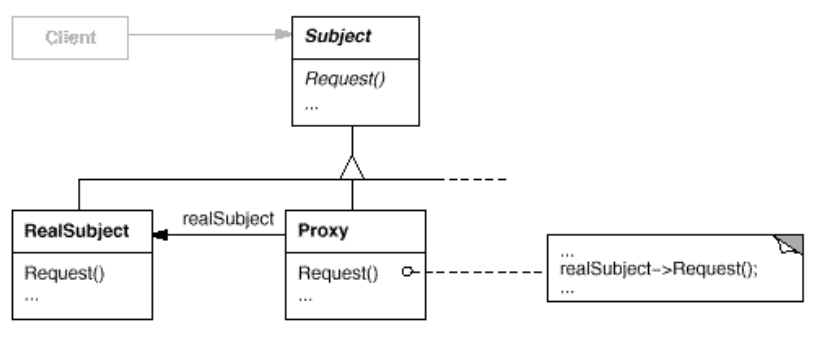
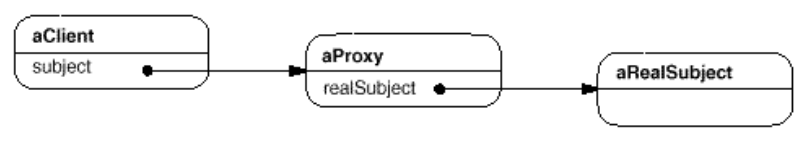
- Structure:
- Participants:
- Proxy
- maintains a reference that lets the proxy access the real subject. Proxy may refer to a Subject if the RealSubject and Subject interfaces are the same.
- provides an interface identical to Subject’s so that a proxy can by substituted for the real subject.
- controls access to the real subject and may be responsible for creating and deleting it.
- other responsibilities depend on the kind of proxy:
- remote proxies are responsible for encoding a request and its arguments and for sending the encoded request to the real subject in a different address space.
- virtual proxies may cache additional information about the real subject so that they can postpone accessing it. For example, the ImageProxy from the Motivation caches the real image’s extent.
- protection proxies check that the caller has the access permissions required to perform a request.
- Subject
- defines the common interface for RealSubject and Proxy so that a Proxy can be used anywhere a RealSubject is expected.
- RealSubject
- defines the real object that the proxy represents.
- Proxy
- Collaborations
- Proxy forwards requests to RealSubject when appropriate, depending on the kind of proxy.
- Consequences:
-
- A remote proxy can hide the fact that an object resides in a different address space.
-
- A virtual proxy can perform optimizations such as creating an object on demand.
-
- Both protection proxies and smart references allow additional housekeeping tasks when an object is accessed.
-
- Related Patterns:
- Adapter: An adapter provides a different interface to the object it adapts. In contrast, a proxy provides the same interface as its subject. However, a proxy used for access protection might refuse to perform an operation that the subject will perform, so its interface may be effectively a subset of the subject’s.
- Decorator: Although decorators can have similar implementations as proxies, decorators have a different purpose. A decorator adds one or more responsibilities to an object, whereas a proxy controls access to an object.
Proxies vary in the degree to which they are implemented like a decorator. A protection proxy might be implemented exactly like a decorator. On the other hand, a remote proxy will not contain a direct reference to its real subject but only an indirect reference, such as “host ID and local address on host.” A virtual proxy will start off with an indirect reference such as a file name but will eventually obtain and use a direct reference.
- Code Sample: Proxy
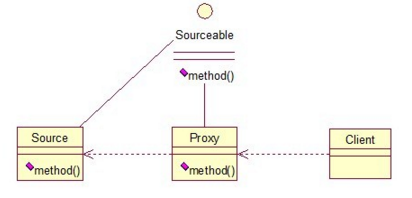
public interface Sourceable {
public void method();
}
public class Source implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("the original method!");
}
}
public class Proxy implements Sourceable {
private Source source;
public Proxy(){
super();
this.source = new Source();
}
@Override
public void method() {
before();
source.method();
atfer();
}
private void atfer() {
System.out.println("after proxy!");
}
private void before() {
System.out.println("before proxy!");
}
}
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sourceable source = new Proxy();
source.method();
}
}
