14. Command
- Intent:
- Encapsulate a request as an object, thereby letting you parameterizeclients with different requests, queue or log requests, and support undoable operations.
- Also Known As:
- Action, Transaction
- Applicability:
- parameterize objects by an action to perform,
- specify, queue, and execute requests at different times.
- support undo.
- support logging changes so that they can be reapplied in case of a system crash.
- structure a system around high-level operations built on primitives operations.
- Structure:
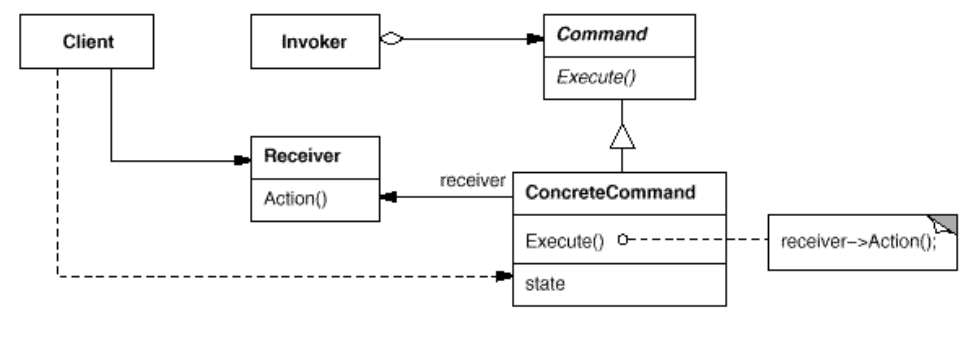
- Participants:
- Command
- declares an interface for executing an operation.
- ConcreteCommand
- defines a binding between a Receiver object and an action.
- implements Execute by invoking the corresponding operation(s) on Receiver.
- Client
- creates a ConcreteCommand object and sets its receiver.
- Invoker
- asks the command to carry out the request.
- Receiver
- knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out a request. Any class may serve as a Receiver.
- Command
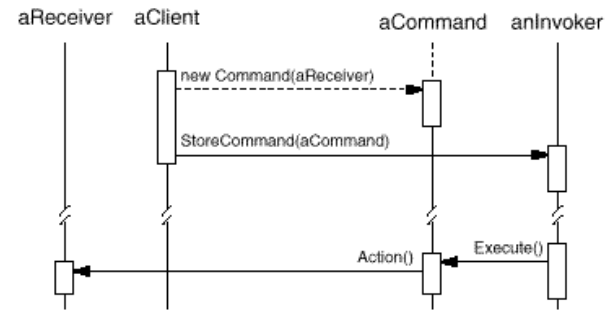
- Collaborations
- The client creates a ConcreteCommand object and specifies its receiver.
- An Invoker object stores the ConcreteCommand object.
- The invoker issues a request by calling Execute on the command. When commandsare undoable, ConcreteCommand stores state for undoing thecommand prior to invoking Execute.
- The ConcreteCommand object invokes operations on its receiver to carryout the request.
- Consequences:
- 1.Command decouples the object that invokes the operation from the one that knows how to perform it.
- 2.Commands are first-class objects.
- 3.You can assemble commands into a composite command.
- 4.It’s easy to add new Commands
- Related Patterns:
- A Composite can be used to implement MacroCommands.
- A Memento can keep state the command requires to undo its effect.
- A command that must be copied before being placed on the history list acts as a Prototype.
- Code Sample: Command
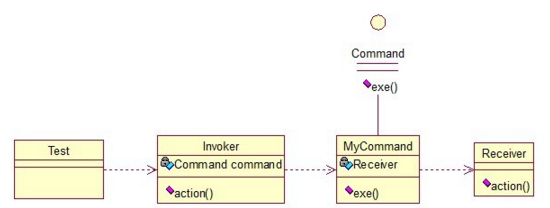
public interface Command {
public void exe();
}
public class MyCommand implements Command {
private Receiver receiver;
public MyCommand(Receiver receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void exe() {
receiver.action();
}
}
public class Receiver {
public void action(){
System.out.println("command received!");
}
}
public class Invoker {
private Command command;
public Invoker(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void action(){
command.exe();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Receiver receiver = new Receiver();
Command cmd = new MyCommand(receiver);
Invoker invoker = new Invoker(cmd);
invoker.action();
}
}
