15. Interpreter
- Intent:
- Given a language, define a represention for its grammar along with an interpreter that uses the representation to interpret sentences in the language.
- Applicability:
- the grammar is simple.
- efficiency is not a critical concern.
- Structure:
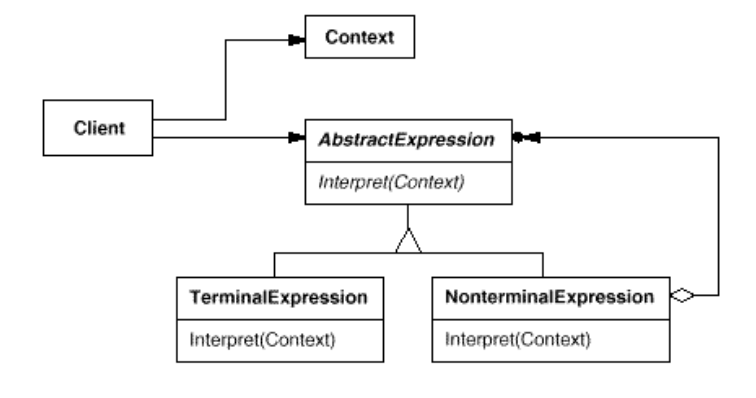
- Participants:
- AbstractExpression
- declares an abstract Interpret operation that is common to all nodes in the abstract syntax tree.
- TerminalExpression
- implements an Interpret operation associated with terminal symbols in the grammar.
- an instance is required for every terminal symbol in a sentence.
- NonterminalExpression
- maintains instance variables of type AbstractExpression for each of the symbols R 1 through R n .
- implements an Interpret operation for nonterminal symbols in the grammar. Interpret typically calls itself recursively on the variables representing R 1 through R n .
- Context
- contains information that’s global to the interpreter.
- Client
- builds (or is given) an abstract syntax tree representing a particular sentence in the language that the grammar defines. The abstract syntax tree is assembled from instances of the NonterminalExpression and TerminalExpression classes.
- invokes the Interpret operation.
- AbstractExpression
- Collaborations
- The client builds (or is given) the sentence as an abstract syntaxtree of NonterminalExpression and TerminalExpression instances. Then the client initializes the context and invokes the Interpretoperation.
- Each NonterminalExpression node defines Interpret in terms of Interpret on each subexpression. The Interpret operation of each TerminalExpression defines the base case in the recursion.
- The Interpret operations at each node use the context to store and access the state of the interpreter.
- Consequences:
- 1.It’s easy to change and extend the grammar.
- 2.Implementing the grammar is easy.
- 3.Complex grammars are hard to maintain.
- 4.Adding new ways to interpret expressions.
- Related Patterns:
- Composite The abstract syntax tree is an instance of the Composite pattern.
- Flyweight shows how to share terminal symbols within the abstract syntaxtree.
- Iterator The interpreter can use an Iterator to traverse the structure.
- Visitor can be used to maintain the behavior in each node in the abstract syntaxtree in one class.
- Code Sample: Interpreter
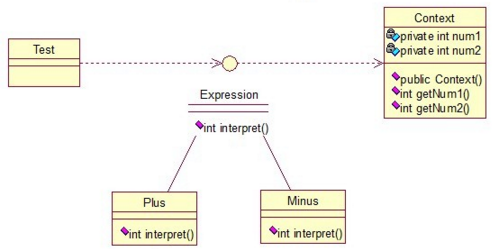
public interface Expression {
public int interpret(Context context);
}
public class Plus implements Expression {
@Override
public int interpret(Context context) {
return context.getNum1()+context.getNum2();
}
}
public class Minus implements Expression {
@Override
public int interpret(Context context) {
return context.getNum1()-context.getNum2();
}
}
public class Context {
private int num1;
private int num2;
public Context(int num1, int num2) {
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
}
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public void setNum1(int num1) {
this.num1 = num1;
}
public int getNum2() {
return num2;
}
public void setNum2(int num2) {
this.num2 = num2;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3+8-1
int result = new Minus().interpret((new Context(new Plus()
.interpret(new Context(3, 8)), 1)));
System.out.println(result);
}
}
