16. Iterator
- Intent:
- Provide a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation.
- Also Known As:
- Cursor
- Applicability:
- to access an aggregate object’s contents without exposing its internal representation.
- to support multiple traversals of aggregate objects.
- to provide a uniform interface for traversing different aggregatestructures (that is, to support polymorphic iteration).
- Structure:
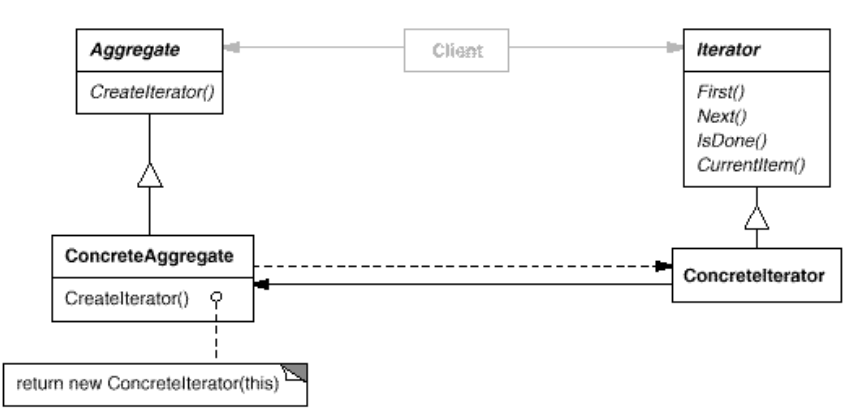
- Participants:
- Iterator
- defines an interface for accessing and traversing elements.
- implements the Iterator interface.
- keeps track of the current position in the traversal of the aggregate.
- Aggregate
- defines an interface for creating an Iterator object.
- ConcreteAggregate
- implements the Iterator creation interface to return an instance of the proper ConcreteIterator.
- Iterator
- Collaborations
- A ConcreteIterator keeps track of the current object in the aggregate and can compute the succeeding object in the traversal..
- Consequences:
- 1.It supports variations in the traversal of an aggregate.
- 2.Iterators simplify the Aggregate interface.
- 3.More than one traversal can be pending on an aggregate.
- Related Patterns:
- Composite:Iterators are often applied to recursive structures such as Composites.
- Factory Method:Polymorphic iterators rely on factory methods to instantiate the appropriate Iterator subclass.
- Memento is often used in conjunction with the Iterator pattern. An iterator can use a memento to capture the state of an iteration. The iteratorstores the memento internally.
- Code Sample: Iterator
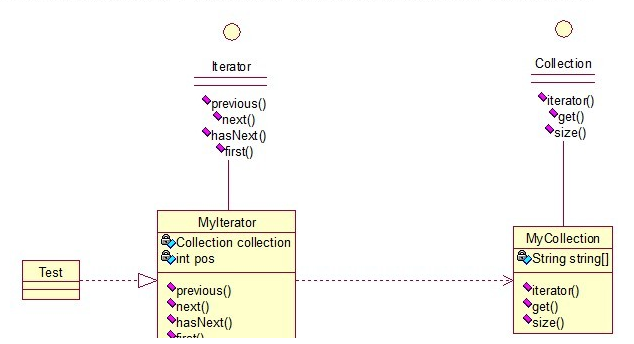
public interface Collection {
public Iterator iterator();
public Object get(int i);
public int size();
}
public interface Iterator {
public Object previous();
public Object next();
public boolean hasNext();
public Object first();
}
public class MyCollection implements Collection {
public String string[] = {"1","2","3","4","5"};
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new MyIterator(this);
}
@Override
public Object get(int i) {
return string[i];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return string.length;
}
}
public class MyIterator implements Iterator {
private Collection collection;
private int pos = -1;
public MyIterator(Collection collection){
this.collection = collection;
}
@Override
public Object previous() {
if(pos > 0){
pos--;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public Object next() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
pos++;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object first() {
pos = 0;
return collection.get(pos);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection collection = new MyCollection();
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
